Ice
Ice is frozen water, solid state of H2O, in normal conditions on the surface of the Earth considered as mineral (while water – H2O in liquid state is not a mineral), freezing/melting point depends on pressure level and is 0 point in Celsius temperature scale.
Ice properties:
- System: Hexagonal
- Hardness (Mohs scale) 1 ½
- colour : colourless to white, pale blue to greenish-blue in thick layers
- Streak : white
- Fracture: conchoidal
- Lustre: vitreous
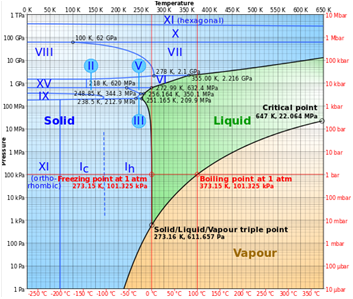
- Density 0,9167 g/cm3 measured, 0,93 calculated (Fig. 3)
- Diamagnetic
Types of ice:
- snow, snowflakes
- ice pellets, hail
- feather ice
- firn
- glacier ice
- sea ice
- water ice
Under conditions other than normal on the surface of the Earth (in space, in laboratory) there are several ice crystallographic variants, these variations also exhibit distinctive physical characteristics.



 This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.
This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.