Opady atmosferyczne
Opady atmosferyczne to woda w postaci ciekłej lub stałej, spadająca z chmur i opadająca na powierzchnię. Opady ciekłe to mżawka i deszcz, opady stałe to śnieg i grad. Opad następuje, gdy rosnące w chmurze krople stają się tak duże, że opadają pod wpływem własnego ciężaru.
Opad to kluczowy czynnik rozwoju roślin, w tym upraw.
Obszary pustynne charakteryzują się ekstremalnie niskimi wartościami opadów.
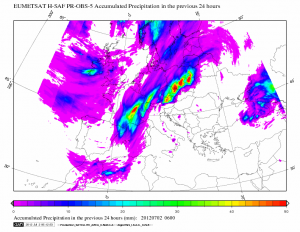
Ilustracja obrazuje poziom opadów, obserwowany z satelity w dniu 2 czerwca 2017 roku nad Europą. Ten rodzaj mapy opadów jest używany do testowania prognoz pogody w oparciu o modele.


 This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.
This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.