Esker
a long ridge built from diagonally layered sands and gravels with waving crest (Fig. 1) or a series of elongated hills created by meltwater flowing through subglacial (subglacial eskers) or englacial (englacial eskers) channels or along open crevices on a glacier’s surface (supraglacial eskers). Subglacial eskers are often located within subglacial trough. Most often, they are perpendicular to the front of the glacier or ice sheet, which created them.
- Fig. 1. An esker close to Gatschof, Mecklenburg Lake Plateau (public domain)
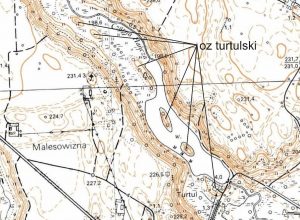
- Fig. 2. Turtulan Esker, a series of hills at the bottom of a subglacial trough. (Suwałki Lakeland) (Geoportal).
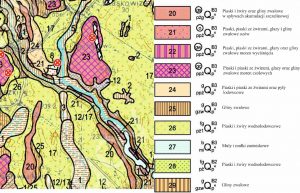
- Fig.3. Turtulian esker , the hills are marked as „21”. SMGP 1:50000 Ark.72 Jeleniewo.
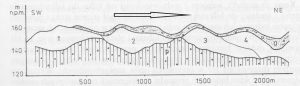
- Fig. 4. Lateral cross section of esker. P – bedrock; 1,2,3,4 – hills of esker in the order of creation; a – till cover; the arrow indicates the retreat of the glacial ice sheet. (Lindner (ed) 1992).



 This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.
This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.