Внешнее ядро
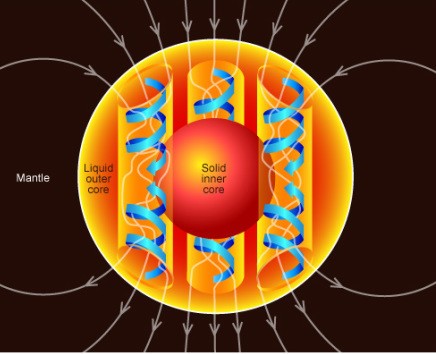
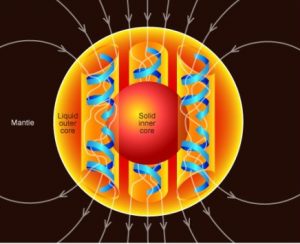
Внешнее ядро — это слой Земли, расположенный между внутренним ядром и мантией Земли. Оно состоит в основном из железа и никеля, которые из-за преобладающего низкого давления, чем во внутреннем ядре, находятся в жидкой состоянии.
Разница температур, химического состава и давления внутри внешнего ядра вызывают конвективное движение жидкости. Кроме того, сила эффекта Кориолиса организует это движение в столбцы, параллельные оси вращения Земли. Электрический ток, генерируемый в каждом из столбцов, создает их магнитное поле, нацеленное в одном и тем же направлении. Это вызывает сложение магнитных полей и образование общего геомагнитного поля, которое простирается далеко в космос и защищает атмосферу нашей планеты от солнечного ветра.


 This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.
This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.