Jądro zewnętrzne
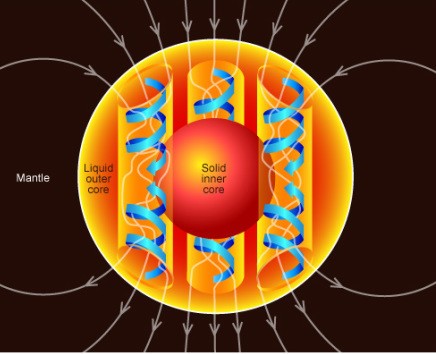
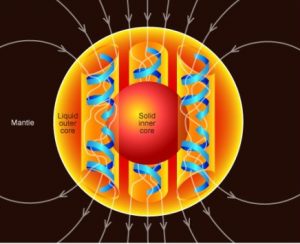
Jądro zewnętrzne to warstwa Ziemi położona pomiędzy jądrem wewnętrznym a ziemskim płaszczem. Składa się głównie z żelaza oraz niklu, które z powodu panującego niższego ciśnienia niż w jądrze wewnętrznym są w postaci płynnej.
Różnice w temperaturze, składzie chemicznym i ciśnieniu wewnątrz jądra zewnętrznego powodują ruch konwekcyjny płynu. Dodatkowo efekt siły Coriolisa porządkuje ten ruch w kolumny równoległe do osi obrotu Ziemi. Prąd elektryczny wytwarzany w każdej z kolumn generuje ich pole magnetyczne, skierowane w tę samą stronę. To powoduje sumowanie się efektu pól magnetycznych i powstanie całkowitego pola geomagnetycznego, które rozciąga się daleko w przestrzeń kosmiczną oraz chroni atmosferę naszej planety przed wiatrem słonecznym.


 This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.
This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.