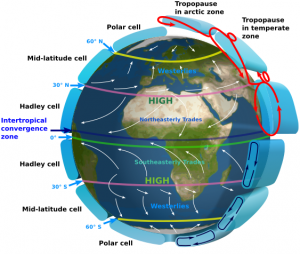
The Ferrel cell
The Ferrel cell is the average motion of air in the mid-latitudes.occurs at higher latitudes (between 30 degrees and 60 degrees N and 30 degrees and 60 degrees S.
In the Ferrel cell, air flows poleward and eastward near the surface and equatorward and westward at higher altitudes; this movement is the reverse of the airflow in the Hadley cell. The Ferrel Cell plays a major part in the poleward energy (mainly heat) transport.


 This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.
This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.