Carbon capture and storage
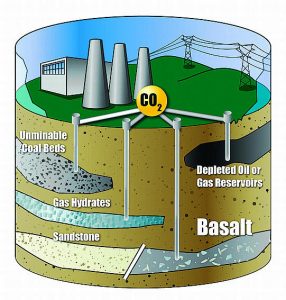
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is an emission reduction process designed to prevent large amounts of carbon dioxide from being released into the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide from power-plant combustion and other industrial sources that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere is captured, compressed and injected into underground geologic formations for safe, secure and permanent storage.
The CCS chain consists of three parts; capturing the carbon dioxide, transporting the carbon dioxide, and securely storing the carbon dioxide emissions, underground in depleted oil and gas fields or deep saline aquifer formations.
The greatest environmental risk associated with CCS relates to the long term storage of the captured CO2. Leakage of CO2, either gradual or in a catastrophic leakage (e.g. due to an earthquake) , could negate the initial environmental benefits of capturing and storing CO2 emissions and may also have harmful effects on human health.


 This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.
This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.