Photosynthesis
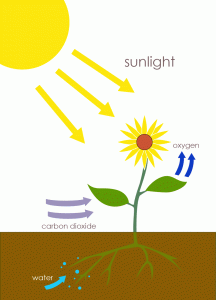
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use the energy from sunlight to produce organic material (which they store), as well as oxygen (which they release into the atmosphere) from carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). Animals cannot do this and therefore have to eat plants or other animals lower in the food chain to get energy. Plants perform photosynthesis using the green pigment chlorophyll.
Photosynthesis is largely responsible for producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth’s atmosphere, and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth. The building and breaking of carbon-based material — from carbon dioxide to complex organic molecules (photosynthesis) then back to carbon dioxide (respiration) — is part of what is commonly called the global carbon cycle.
- ZooFari
- At09kg



 This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.
This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.