Subarctic
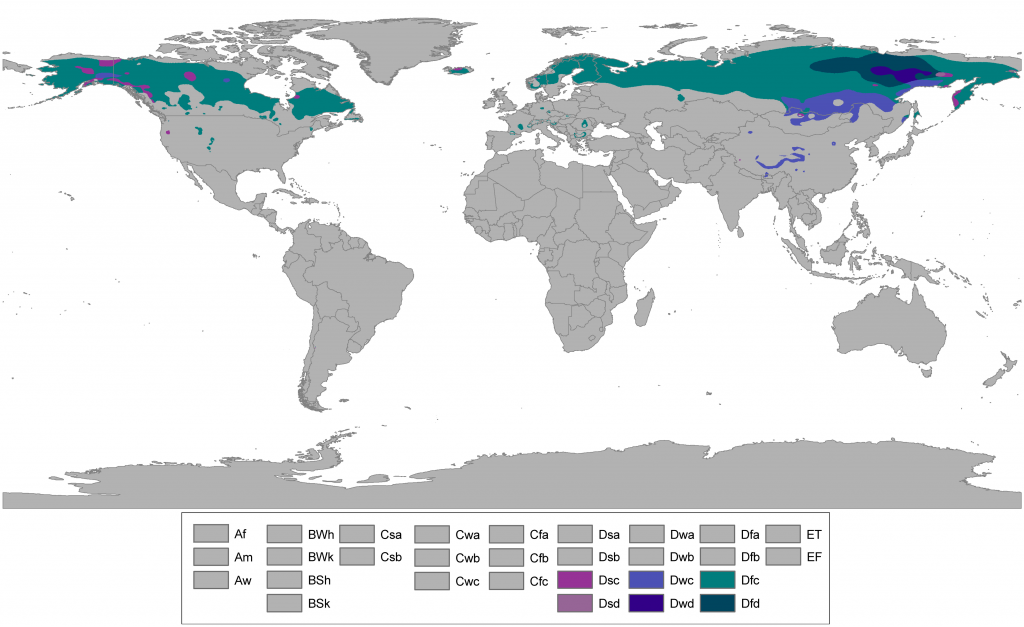
The Subarctic is a region in the Northern Hemisphere immediately south of the Arctic and covering much of Alaska, Canada, Iceland, the north of Scandinavia, Siberia, and the Shetland Islands. Generally, subarctic regions fall between 50°N and 70°N latitude, depending on local climates.
Monthly temperatures are above 10 °C (50 °F) for at least one and at most three months of the year. Subarctic regions are often characterised by taiga forest vegetation. Agriculture is mainly limited to animal husbandry, though in some areas barley can be grown. Among large mammals living in subarctic zone, there are elk, moose, bears, reindeer, and wolves. Canada and Siberia are very rich in minerals, notably nickel, molybdenum, cobalt, lead, zinc and uranium.
Except for those areas adjacent to warm ocean currents, there is almost always continuous permafrost due to the very cold winters.
- Peel, M. C., Finlayson, B. L., and McMahon, T. A. (University of Melbourne)
- NOAA



 This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.
This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.