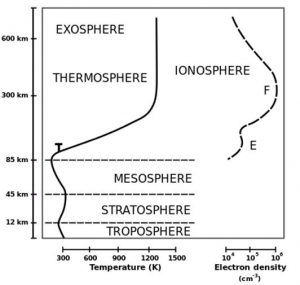
Ionosphère
L’ionosphère fait partie de la haute atmosphère et s’étend de 80 à 1000 km au-dessus de la surface de la Terre, partiellement ionisée.
Les rayonnements (solaires ou cosmiques) avec des longueurs d’onde plus courtes que les UV ont suffisamment d’énergie pour séparer un électron d’un atome ou d’une molécule neutre, qui devient alors un ion.
En raison de la plus faible densité de l’atmosphère supérieure, de tels électrons libres peuvent exister pendant une courte période de temps avant qu’ils ne se heurtent à des ions se recombinant en atomes neutres. Tout changement du rayonnement solaire et cosmique affecte les propriétés de l’ionosphère, influençant ainsi le f. propagation d’ondes radio utilisées pour la communication et la navigation.
Illustration: wikipedia.org


 This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.
This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.