Poziom amplitudy zerowej
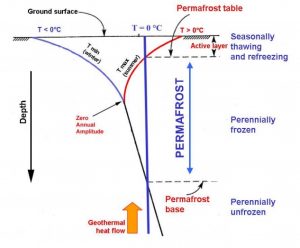
Poziom amplitudy zerowej to głębokość liczona od powierzchni gruntu, gdzie ustają wahania temperatury wieloletniej zmarzliny.
W zmarzlinie górna warstwa znana jako „warstwa czynna”, podlega na zmianę topnieniu i zamarzaniu przez cały rok. Pod tą warstwą, temperatura spada poniżej 0°C, a zatem grunt jest stale zamrożony. Idąc dalej w głąb gruntu, roczne wahania temperatur stają się coraz mniejsze i wreszcie poniżej określonego poziomu temperatura pozostaje stała w ciągu całego roku. Punkt, w którym roczna zmienność temperatury jest mniejsza niż 0,1°C jest definiowany poziom amplitudy zerowej.
Głębokość tego punktu może się wahać między 10 a 20 metrów pod powierzchnią, zależy to od warunków klimatycznych i rodzaju osadów. Poniżej poziomu amplitudy zerowej temperatura stopniowo wzrasta wraz ze wzrostem głębokości, co spowodowane jest oddziaływaniem ciepła geotermalnego, i na pewnym poziomie ponowne wzrasta powyżej 0°, co wyznacza dolną granicę (spąg) zmarzliny.



 This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.
This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.