Konwencja Berneńska
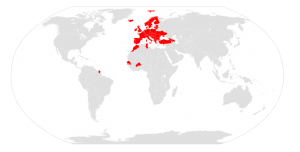
Konwencja Berneńska (Konwencja o ochronie gatunków dzikiej flory i fauny europejskiej oraz ich siedlisk) jest wiążącym instrumentem prawnym stosowanym w ochronie dzikich roślin i zwierząt. Obecnie 47 państw w Europie i 4 w Afryce ratyfikowały ten międzynarodowy traktat przyjęty w 1979 roku. Sygnatariusze zobowiązują się do regulowania między innymi zakresu i sposobu pozyskiwania dzikich zwierząt (np. legalne polowania), a także dostępu do siedlisk. Konwencja ma na celu zagwarantowanie takiego zarządzania środowiskiem, które zahamuje spadek różnorodności biologicznej.



 This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.
This project (EDU-ARCTIC) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 710240. The content of the website is the sole responsibility of the Consortium and it does not represent the opinion of the European Commission, and the Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of information contained.